- Преподаватель: Ольга Валентиновна Жукова
- Преподаватель: Айя Кореневская
- Преподаватель: Мария Николаевна Острецова
- Преподаватель: Алексей Леонидович Савастенко
- Преподаватель: Галина Павловна Терещенко
- Преподаватель: РОМАН АВАКОВИЧ ХАНФЕРЬЯН
- Преподаватель: Марина Станиславовна Артемьева
The discipline "Endocrinology" in the
specialty 31.05.01 "Medical business" is taught in Russian and
English at the Department of hospital therapy with courses in Endocrinology,
Hematology and Clinical laboratory diagnostics (CLD) of the RUDN University Medical
Institute.
- Преподаватель: Марина Робертовна Александрова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Кочемасова
- Преподаватель: Ирина Алексеевна Курникова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Антоновна Мелешкевич
- Преподаватель: Леонид Юльевич Моргунов
- Преподаватель: Рита Романовна Политидис
- Преподаватель: Павел Сергеевич Попов
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Николаевна Кабаева
- Преподаватель: Егор Геннадьевич Чмутин
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Александровна Гительзон
- Преподаватель: Марина Михайловна Зубаркина
Карантинная травматология
- Преподаватель: Медетбек Джумабекович Абакиров
- Преподаватель: Магомед Абдулхабирович Абдулхабиров
- Преподаватель: Расул Николаевич Алиев
- Преподаватель: Данила Алексеевич Ананьин
- Преподаватель: Евгений Александрович Беляк
- Преподаватель: Максим Федорович Лазко
- Преподаватель: Михаил Александрович Панин
- Преподаватель: Алексей Петрович Призов
- Преподаватель: Денис Владимирович Римашевский
- Преподаватель: Мухаммад Таблиханович Сампиев
- Преподаватель: Александр Владимирович Фролов
- Преподаватель: Виктор Александрович Жернов
- Преподаватель: Лариса Петровна Васильева
- Преподаватель: Юлия Шамилевна Гущина
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Ляпунова
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Михайловна Шимкевич
- Преподаватель: Любовь Анатольевна Горева
- Преподаватель: Марина Алексеевна Ефремовцева
- Преподаватель: Никита Михайлович Поваляев
- Преподаватель: Светлана Александровна Рачина
- Преподаватель: Андрей Анатольевич Шаваров
- Преподаватель: Елена Курбановна Шаварова
- Преподаватель: Валерий Валентинович Бекреев
- Преподаватель: Александр Борисович Дымников
- Преподаватель: Дарья Вячеславовна Жучкова
- Преподаватель: Сергей Юрьевич Иванов
- Преподаватель: Сергей Георгиевич Ивашкевич
- Преподаватель: Элеонора Владимировна Ким
- Преподаватель: КОНСТАНТИН КОНСТАНТИНОВИЧ КОБЕЦ
- Преподаватель: Роман Фларидович Мухаметшин
- Преподаватель: Вадим Дмитриевич Труфанов
Psychology, pedagogy course for second-year students
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Геннадьевна Лазукова
- Преподаватель: Юлия Вадимовна Ставцева
- Преподаватель: Гаджимурад Магомедович Запиров
- Преподаватель: Роман Алексеевич Пархоменко
- Преподаватель: Мария Владимировна Подольская
- Преподаватель: Наталья Владимировна Харченко
- Преподаватель: Николай Иванович Головцов
- Преподаватель: МУХАММАД ИСКАНДАР
- Преподаватель: Сергей Петрович Карнилович
The purpose of the "Ophthalmology" is the formation of scientific knowledge in ophthalmology and the ability to detect eye pathology, to prevent eye diseases and provide first aid to ophthalmological patients
- Преподаватель: Елена Сергеевна Беляева
- Преподаватель: Галина Николаевна Душина
- Преподаватель: Ксения Александровна Казакова
- Преподаватель: Винод Кумар
This course was developed for English groups especially.
- Преподаватель: Данила Алексеевич Ананьин
The objectives of the discipline are to help students study the clinical anatomy and physiology of the larynx, to study and develop methods for studying the larynx, to teach diagnosis, treatment, prevention and rehabilitation in acute and chronic laryngeal diseases. Also, study of modern aspects of a tracheotomy, as a technique of surgical treatment.
Aims of the discipline:
- study of normal and pathological anatomy, as well as physiology of the larynx;
- study of the etiology, mechanisms of development and outcomes of acute and chronic laryngeal diseases;
- analysis of clinical manifestations of the most common acute and chronic laryngeal diseases;
- study of the main methods of diagnosing the larynx;
- study principles of pathogenetic therapy and prevention of acute and chronic larynx diseases;
- study of methods of tracheotomy, possible complications during tracheotomy.
- Преподаватель: Антонина Валерьевна Бицаева
- Преподаватель: Ирина Анатольевна Коршунова
- Преподаватель: Анна Ильинична Чернолев
The objectives of the discipline is to help students study and learn methods of examining ENT organs, to teach diagnosis, treatment, prevention and rehabilitation of ear, nose and throat diseases.
Aims of the discipline:
- study of normal and pathological anatomy, as well as physiology of ENT organs;
- study of the etiology, mechanisms of development and outcomes of various diseases of ENT – organs;
- analysis of clinical manifestations of the most common diseases of ENT – organs;
- study of the main methods of diagnosis of ENT – pathology;
- introduction with the principles of pathogenesis therapy and prevention of ENT diseases.
- Преподаватель: Антонина Валерьевна Бицаева
- Преподаватель: Ирина Анатольевна Коршунова
- Преподаватель: Анна Ильинична Чернолев
Aim of the discipline is students’ acquisition of knowledge in the field of molecular genetics, which is necessary for the formation of the scientific worldview and practical activities of the physician.
- Преподаватель: Мадина Мухамедовна Азова
- Преподаватель: Амира Аит Аисса
- Преподаватель: Юлия Николаевна Рябенко
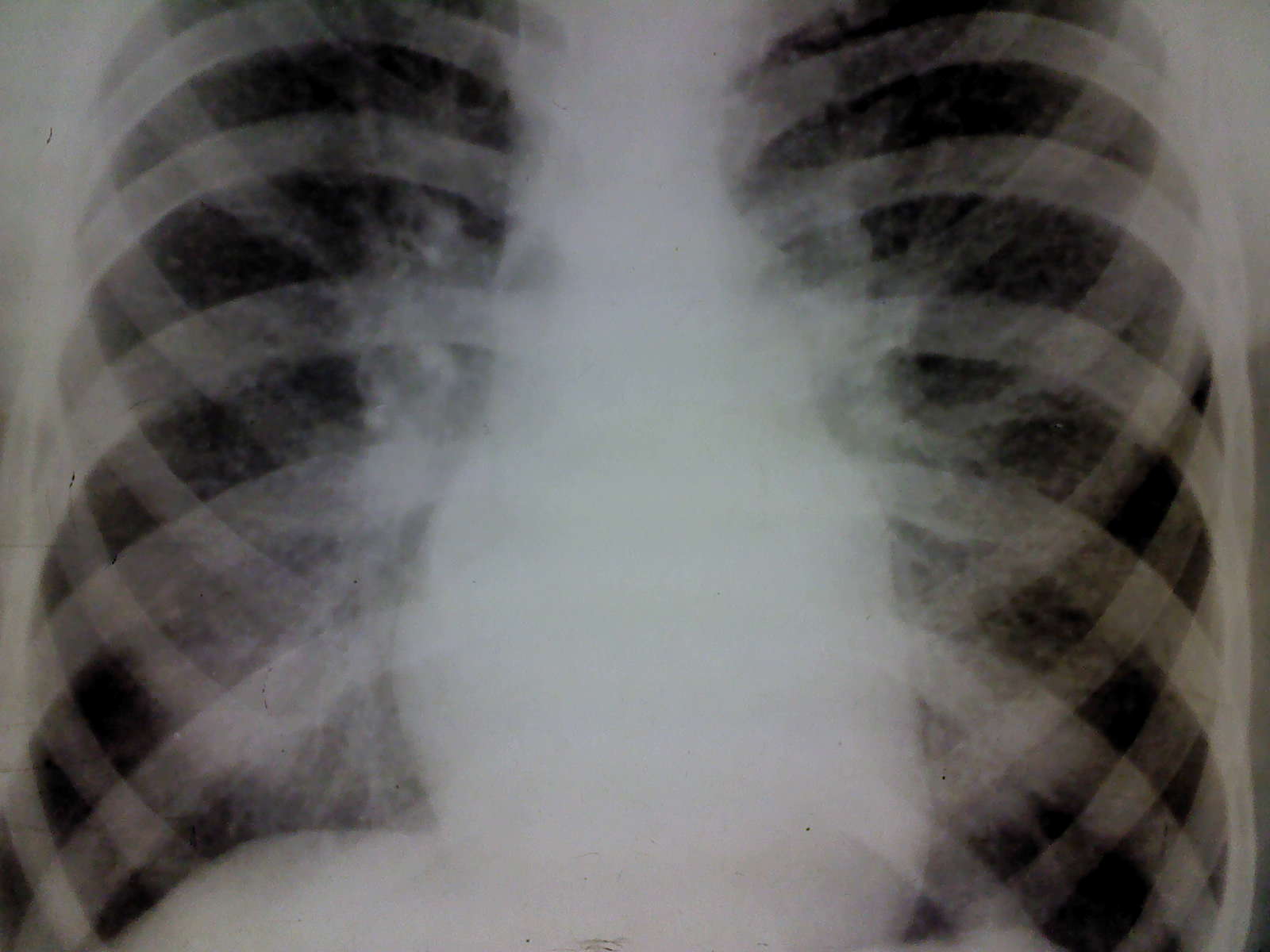
The aim of the Course is to inform the students of the 3d course about the main terms and principles of Radiology used for diagnostics of pulmonary, cardiovascular, digestive and skeleto-mascular systems.
After completion of the course students should be able to distinguish major syndromes of those diseases on radiographs.
They should also know the potential of other diagnostic imaging modalities.
- Преподаватель: Гаджимурад Магомедович Запиров
- Преподаватель: Роман Алексеевич Пархоменко
- Преподаватель: Мария Владимировна Подольская
- Преподаватель: Наталья Владимировна Харченко
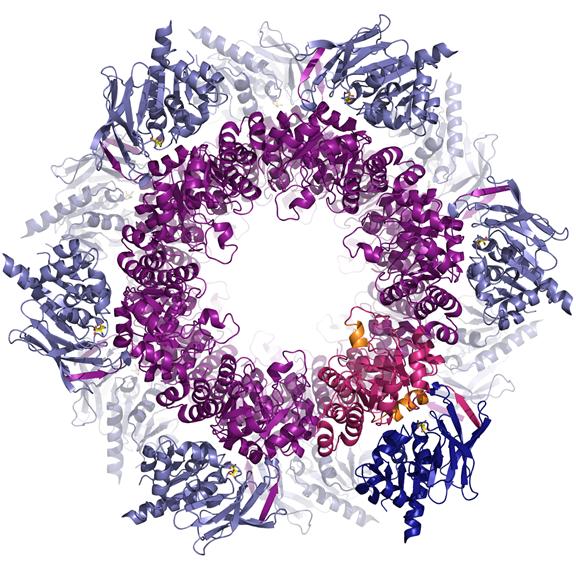
Medical Enzymology - Elective Course for Medical Students made by the Berezov T.T. Department of Biochemistry.
- Преподаватель: Марсель Минивакилевич Башаров
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Дмитриевич Жданов
- Преподаватель: Вероника Игоревна Иванова-Радкевич
- Преподаватель: Елена Валентиновна Калинина
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Александровна Лобаева
- Преподаватель: Елена Васильевна Лукашева
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Владиславовна Неборак
- Преподаватель: Вадим Сергеевич Покровский
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Рыскина
- Преподаватель: Николай Николаевич Чернов
- Преподаватель: Марина Станиславовна Артемьева
- Преподаватель: Логинова Екатерина Владимировна 1042180039
- Преподаватель: Said M. Semyatov
- Преподаватель: Игорь Александрович Алеев
- Преподаватель: Сергей Владиславович Апресян
- Преподаватель: Мария Павловна Архипова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Геннадьевич Арютин
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Николаевна Ахматова
- Преподаватель: Анна Валерьевна Борисова
- Преподаватель: Челеби Гасанович Гагаев
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Галина
- Преподаватель: Александр Сергеевич Гаспаров
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Доронина
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Дмитриевна Дубинская
- Преподаватель: Армен Олегович Духин
- Преподаватель: Василий Владимирович Ермаков
- Преподаватель: Фарида Мухарбиевна Есенеева
- Преподаватель: Нина Ивановна Захарова
- Преподаватель: Татевик Ншановна Зулумян
- Преподаватель: Лилия Андреевна Кайгородова
- Преподаватель: Сетонде Ромео Дамиен Коннон
- Преподаватель: Игорь Николаевич Костин
- Преподаватель: Ольга Алексеевна Кузнецова
- Преподаватель: Марина Георгиевна Лебедева
- Преподаватель: Милана Султановна Лологаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Борисовна Лукановская
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Вадимовна Минаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Молчанова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Сергеевич Новгинов
- Преподаватель: Владислава Александровна Новикова
- Преподаватель: Агамурад Акмамедович Оразмурадов
- Преподаватель: Мекан Рахимбердыевич Оразов
- Преподаватель: Ирина Михайловна Ордиянц
- Преподаватель: Роман Евгеньевич Орехов
- Преподаватель: Александр Георгиевич Погасов
- Преподаватель: Виктор Евсеевич Радзинский
- Преподаватель: Фатима Умаровна Рамазанова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Викторовна Смирнова
- Преподаватель: Алина Викторовна Соловьева
- Преподаватель: Залина Михайловна Сохова
- Преподаватель: Мухаммедназар Аманович Союнов
- Преподаватель: Надежда Михайловна Старцева
- Преподаватель: Лилия Равильевна Токтар
- Преподаватель: Халид Хаддад
- Преподаватель: Марина Борисовна Хамошина
- Преподаватель: Елена Михайловна Курмелева
Discipline objective: acquiring and imroving of new knowledge as well as application of distance technologies in health practice at:
· emergency and planned tele-consulting and medical care for patients who are at a great distance from a consultant-doctor (especially in cases of emergency);
· tele-education and qualifications improvement for medical staff;
· prenatal care and patients with chronic diseases,
· home monitoring hospital patients;
· Monitoring of mobile patients with personal life support devices.
- Преподаватель: Майя Александровна Амчеславская
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Ляпунова
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Михайловна Шимкевич
- Преподаватель: Наталья Агафоновна Дрожжина
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Ефимушкина
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Константиновна Застрожина
- Преподаватель: Людмила Витальевна Максименко
- Преподаватель: Анна Владимировна Фомина
Public Health and Healthcare, Healthcare Economics for medical students (3,4 year - specialty "General Medicine")
- Преподаватель: Орабийи Омолара Мотолани 1042205125
- Преподаватель: Адхена Бейене Мересса 1042215046
- Преподаватель: Елена Валерьевна Каверина
- Преподаватель: Иван Анатольевич Кротов
- Преподаватель: Мд Шалим Реза
- Преподаватель: Анна Владимировна Фомина
The purpose of teaching immunology to students of the specialty “Medicine” is to create in them modern ideas about the physiological bases of the immune system, its functioning at the cellular and molecular levels, adaptive and acquired defense mechanisms, etiology and pathogenesis of immunopathological processes, including immunodependent and allergic diseases as well as modern methods of clinical, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, traditional and innovative areas in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of patients with immuno-pathology.
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Левкова
- Преподаватель: Мария Николаевна Острецова
- Преподаватель: Алексей Леонидович Савастенко
- Преподаватель: Реваз Исмаилович Сепиашвили
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Александровна Славянская
- Преподаватель: Евгения Львовна Панова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Сергеевна Сорокина

- Преподаватель: Елена Николаевна Белобородова
- Преподаватель: Ольга Олеговна Винокурова
- Преподаватель: Сергей Леонидович Вознесенский
- Преподаватель: Светлана Юрьевна Дегтярева
- Преподаватель: Вера Николаевна Зимина
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Игоревна Кулабухова
- Преподаватель: Александра Витальевна Соловьёва
The purpose of the discipline is to study the theoretical foundations of classical and contemporary Nutrition, formation of students' knowledge of the physiological and clinical picture of the processes occurring in the human body.
- Преподаватель: Алексей Владимирович Гальченко
- Преподаватель: Андрей Робертович Грабеклис
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Викторовна Коробейникова
- Преподаватель: Юлия Николаевна Лобанова
- Преподаватель: МАРИЯ АЛЕКСАНДРОВНА МУМРИКОВА
- Преподаватель: Елена Валерьевна Рылина
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Викторович Скальный
- Преподаватель: Андрей Анатольевич Скальный
- Преподаватель: Любовь Николаевна Чернова
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Лукьянова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Ляпунова
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Михайловна Шимкевич
Studying the role of medical elementology in the general system of natural sciences. Study different approaches to determine the basic concepts of the biological classification of chemical elements. Formation of the concept of the role of chemical elements in the functioning of the organism. Formation of the idea of chemical elements as bioelements.
Main issues: Definition of medical elementology. Position in the system of sciences. Structural and organizational levels of living matter. The concept of bioelements. Primary (simple and complex) and secondary bioelements. Organic and inorganic bio-elements. Chemical element as a component of the submolecular level of organization of a living organism. Classification of chemical elements in accordance with their content in the mammalian organism (macroelements, microelements, ultramicroelements). The role of chemical elements in the functioning of the body as the basis for the classification of trace elements. Irreplaceable and toxic trace elements. Conditionally irreplaceable and toxic elements. Nutrients. Microelements with undetermined biological activity.
- Преподаватель: Ольга Павловна Айсувакова
- Преподаватель: Алексей Владимирович Гальченко
- Преподаватель: Андрей Робертович Грабеклис
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Викторовна Коробейникова
- Преподаватель: Юлия Николаевна Лобанова
- Преподаватель: МАРИЯ АЛЕКСАНДРОВНА МУМРИКОВА
- Преподаватель: Елена Валерьевна Рылина
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Викторович Скальный
- Преподаватель: Андрей Анатольевич Скальный
- Преподаватель: Любовь Николаевна Чернова
Obstetrics (from the French coucher – lie on the back, e.g. to help during childbirth, in the English-speaking countries, obstetrics – from the Latin obstare – to stand beside) is the branch of human activity aimed at optimizing the basic biological function – reproduction of its own kinds.
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynaecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynaecology (OB/GYN) which is a surgical field.
This field is divided into physiological, pathological and operative obstetrics.
- Преподаватель: Логинова Екатерина Владимировна 1042180039
- Преподаватель: Said M. Semyatov
- Преподаватель: Игорь Александрович Алеев
- Преподаватель: Сергей Владиславович Апресян
- Преподаватель: Мария Павловна Архипова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Геннадьевич Арютин
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Николаевна Ахматова
- Преподаватель: Анна Валерьевна Борисова
- Преподаватель: Челеби Гасанович Гагаев
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Галина
- Преподаватель: Александр Сергеевич Гаспаров
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Доронина
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Дмитриевна Дубинская
- Преподаватель: Армен Олегович Духин
- Преподаватель: Василий Владимирович Ермаков
- Преподаватель: Фарида Мухарбиевна Есенеева
- Преподаватель: Нина Ивановна Захарова
- Преподаватель: Татевик Ншановна Зулумян
- Преподаватель: Лилия Андреевна Кайгородова
- Преподаватель: Сетонде Ромео Дамиен Коннон
- Преподаватель: Игорь Николаевич Костин
- Преподаватель: Ольга Алексеевна Кузнецова
- Преподаватель: Марина Георгиевна Лебедева
- Преподаватель: Милана Султановна Лологаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Борисовна Лукановская
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Вадимовна Минаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Молчанова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Сергеевич Новгинов
- Преподаватель: Владислава Александровна Новикова
- Преподаватель: Агамурад Акмамедович Оразмурадов
- Преподаватель: Мекан Рахимбердыевич Оразов
- Преподаватель: Ирина Михайловна Ордиянц
- Преподаватель: Роман Евгеньевич Орехов
- Преподаватель: Александр Георгиевич Погасов
- Преподаватель: Виктор Евсеевич Радзинский
- Преподаватель: Фатима Умаровна Рамазанова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Викторовна Смирнова
- Преподаватель: Алина Викторовна Соловьева
- Преподаватель: Залина Михайловна Сохова
- Преподаватель: Мухаммедназар Аманович Союнов
- Преподаватель: Надежда Михайловна Старцева
- Преподаватель: Лилия Равильевна Токтар
- Преподаватель: Халид Хаддад
- Преподаватель: Марина Борисовна Хамошина
- Преподаватель: Аскольд Владиславович Смирнов
- Преподаватель: Андрей Владимирович Ермолаев
- Преподаватель: Ахмед Абдулбари Амин Махюп 1042165112
- Преподаватель: Зеленова Екатерина Евгеньевна 1042210071
- Преподаватель: Мадина Мухамедовна Азова
- Преподаватель: Амира Аит Аисса
- Преподаватель: Галина Ивановна Мяндина
- Преподаватель: Юлия Николаевна Рябенко
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Владимировна Тарасенко
- Преподаватель: Игорь Иванович Бабиченко
- Преподаватель: Алексей Вадимович Волков
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Анатольевна Ивина
- Преподаватель: Константин Юрьевич Мидибер
- Преподаватель: Константин Аркадьевич Рогов
- Преподаватель: Надежда Анатольевна Соловьева
- Преподаватель: Наталья Сергеевна Цимбалист
- Преподаватель: Игорь Иванович Бабиченко
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Анатольевна Ивина
- Преподаватель: Надежда Анатольевна Соловьева
- Преподаватель: Диана Росина Фамилья Фриас
- Преподаватель: Данила Андреевич Ходжаев
- Преподаватель: Моджисола Ибитайо Даниэл-Абу
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Юрьевна Илларионова
- Преподаватель: Максим Александрович Карпенко
- Преподаватель: Юлия Юрьевна Новикова
- Преподаватель: Павел Александрович Фролов
- Преподаватель: Мустафа Халед
- Преподаватель: Саакова Люсинэ Наириевна 1042190031
- Преподаватель: Александр Владимирович Возжаев
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Алексеевич Клюев
- Преподаватель: Сергей Борисович Фитилев
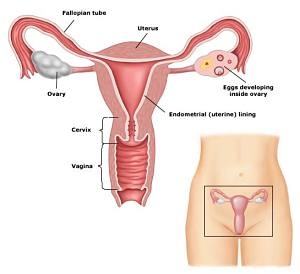
Gynaecology or gynecology (see spelling differences) (the science about woman, from the grec. gyne – a
woman and logos – science) is a medical discipline that studies the normal
physiological activity of the female genital organs and the pathological
processes that arise in them, as well as the prevention and treatment of these pathological
processes.
- Преподаватель: Логинова Екатерина Владимировна 1042180039
- Преподаватель: Said M. Semyatov
- Преподаватель: Игорь Александрович Алеев
- Преподаватель: Анна Валерьевна Борисова
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Доронина
- Преподаватель: Василий Владимирович Ермаков
- Преподаватель: Сетонде Ромео Дамиен Коннон
- Преподаватель: Милана Султановна Лологаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Борисовна Лукановская
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Вадимовна Минаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Константиновна Молчанова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Сергеевич Новгинов
- Преподаватель: Мекан Рахимбердыевич Оразов
- Преподаватель: Роман Евгеньевич Орехов
- Преподаватель: Фатима Умаровна Рамазанова
- Преподаватель: Алина Викторовна Соловьева
- Преподаватель: Халид Хаддад
- Преподаватель: Дарауше Хади Маджед Соуд 1042175165
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Михайлович Аванесов
- Преподаватель: Карэн Анатольевич Аванесов
- Преподаватель: Евгения Николаевна Гвоздикова
- Преподаватель: Сергей Вениаминович Голуб
- Преподаватель: Анна Александровна Дидина
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Валерьевна Игнатова
- Преподаватель: Людмила Аркадьевна Кручинина
- Преподаватель: Зао хоанг Хоанг Нгуен
- Преподаватель: Лада Владимировна Санеева
- Преподаватель: Юрий Георгиевич Седов
- Преподаватель: Далила Али Хайдар
Evidence-based medicine is an approach to
medical practice intended to optimize decision-making by emphasizing the use of
evidence from well-designed and well-conducted research. Although all medicine
based on science has some degree of empirical support, EBM goes further,
classifying evidence by its epistemological strength and requiring that only
the strongest types (coming from meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and randomized
controlled trials) can yield strong recommendations; weaker types (such as from
case-control studies) can yield only weak recommendations. The term was
originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine
and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients. Use
of the term rapidly expanded to include a previously described approach that
emphasized the use of evidence in the design of guidelines and policies that
apply to groups of patients and populations ("evidence-based practice
policies"). It has subsequently spread to describe an approach to
decision-making that is used at virtually every level of health care as well as
other fields (evidence-based practice).

- Преподаватель: Ольга Филипповна Выхристюк
- Преподаватель: Михаил Львович Благонравов
- Преподаватель: Вячеслав Александрович Горячев
- Преподаватель: Алаа А.м. Немер
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Павловна Склифасовская
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Олеговна Шевелева
The purpose of the training: the preparation of a qualified doctor - a specialist with a system of professional competencies, capable and ready for self-employment
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Юрьевна Илларионова
- Преподаватель: Максим Александрович Карпенко
- Преподаватель: Павел Александрович Фролов
The discipline provides current information on the clinical pharmacology of cardiovascular drugs, which are most often
used in outpatient practice. Approaches to the treatment of cardiovascular diseases at outpatient level described according to modern foreign and Russian guidelines.
- Преподаватель: Фрейре Да Сильва Тиаго 1092163187
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Владимировна Митина
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Борисовна Прокофьева
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Ивановна Русанова
- Преподаватель: Николай Владимирович Стуров
- Преподаватель: Андрей Валентинович Сыров
- Преподаватель: Петр Андреевич Гончар
- Преподаватель: Винод Кумар
- Преподаватель: Александр Михайлович Фролов
- Преподаватель: Михаил Александрович Фролов
This course will introduce students to basic principles of epidemiology and key scientific concepts within the field of infectious disease epidemiology. The basic epidemiology part will cover core concepts, including study of epidemic process, infection transmission mechanisms, manifestations of epidemic process, epidemiological methods, disinfection and sterilization, vaccine epidemiology, principles of control and prevention of communicable diseases. The infectious disease epidemiology part will include epidemiology of intestinal, respiratory and contact infections. At the end of the course, students will have a good knowledge for global infectious disease control.
- Преподаватель: Сергей Леонидович Вознесенский
- Преподаватель: Карл Чуквуемека Емероле
- Преподаватель: Анна Владимировна Еремеева
- Преподаватель: Юлия Александровна Климова
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Вадимовна Покровская
- Преподаватель: Раджеш Рохидас Залте
- Преподаватель: Анна Владимировна Листратова
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Сорокина
- Преподаватель: Ольга Анатольевна Стороженко
- Преподаватель: Алексей Алексеевич Феста
The goal is to develop ethnopsychological competence of the students of RUDN UNIVERSITY for the prevention and constructive resolution of ethnic conflicts in the professional, training and household spheres of life.
Objectives of the course:
- get acquainted with theoretical foundations of international communication and tolerance;
- create a view about the psychological characteristics of communication and interaction with different ethnic groups;
- to develop skills of the conflict-free interaction with representatives of various ethnic groups in vocational training and household spheres of life;
- to create conditions for the development of each student’ skills of constructive resolution of ethnic conflicts on the workplace.
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Николаевна Полянская

Infectious disease is a major challenge our society in the developed and developing worlds.
In this course you will study the interaction between microorganisms and their hosts, the processes of infection and how microbes cause disease. This knowledge can then be applied to the development of prevention and therapeutic strategies.
Objectives
1) To acquire an advanced understanding of the etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy of patients with the major infectious diseases :
2) To acquire an advanced understanding of common bacterial, viral, parastic, and other infectious agents and their relationship to clinical infectious syndromes
3) To acquire an advanced understanding of the their differential diagnosis especially with non-infectious disease
4) To acquire a basic understanding of the principles of preventive measures in relationship to infectious disease
- Преподаватель: Сергей Леонидович Вознесенский
- Преподаватель: Карл Чуквуемека Емероле
- Преподаватель: Юлия Александровна Климова
- Преподаватель: Анастасия Вадимовна Покровская
- Преподаватель: Русул Яхья Джасим Яхья Ясим Алабада
- Преподаватель: Ольга Владимировна Ковальчукова
- Преподаватель: Елена Юрьевна Невская
- Преподаватель: Елена Ивановна Полякова
- Преподаватель: Анна Федоровна Степнова
|
1. Course Goals: |
|
· represent current data about the molecular basis of physiological processes; · -to create basic concepts of the course: the relationship between the structure and function of proteins, enzymes, hormones and cell mediators (messengers); · -to introduce students in research methods in molecular physiology; · -to show significance of the molecular processes in the pathogenesis, disease prevention and treatment; · -create a broad foundation of general biological education, that necessary for professional competencies in medical doctors. · - mastering the students in molecular bases of physiological processes; · - development of skills in the differentiation of the main mechanisms of action of biologically active substances; · - Formation of necessary practical skills of using the concept of the first and second messengers in related disciplines. |
|
2. Course Description: |
|
· The properties of ion channels and their role in the formation of RMP and AP, the molecular causes of the accommodation and refractory. · The physiology of synapses. Molecular mechanisms of signal transduction between cells. · Electromechanical coupling in the muscle. The molecular mechanism of muscle contraction, the role of contractile proteins · Molecular properties of chromoproteids and their role in gas exchange. Features of normal and abnormal hemoglobin compounds. The principles of the interaction of receptors and ligands. Metabotropic receptors and cascade of intracellular reactions. The concept of the first and second imessengers · The molecular basis of the reception in the sensory systems. Characteristics of mechanoreceptors · Photoreception and vision. Visual pigments and their properties. Cascade reactions. · Transmembrane transport on template of the molecular mechanisms of intestinal and renal epithelial reabsorbtion |
- Преподаватель: Зарина Важикоевна Бакаева
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Сергеевич Свешников
- Преподаватель: Евгения Александровна Северина
- Преподаватель: Владимир Иванович Торшин
- Преподаватель: Елена Борисовна Якунина
The
aim of studying human physiology is the acquisition by students of the knowledge about the
functioning of various systems of a human organism on the basis of modern
achievements of physiology and also formation with them of professional medical
general culture competence in the problems
of structural organization of the main processes of vital activity of a
human organism.
- Преподаватель: Зарина Важикоевна Бакаева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Леонидовна Романова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Сергеевич Свешников
- Преподаватель: Евгения Александровна Северина
- Преподаватель: Владимир Иванович Торшин
- Преподаватель: Елена Борисовна Якунина
Discipline Examination of Temporary Disability (ETD) is taught as a variable discipline of the professional cycle.
The course aims to master basic concepts and skills in the organization of temporary disability examination in terms of outpatient clinics and in the hospital in Russia.
1 point of credit
(36 class hours).
Language - English.
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Ивановна Русанова
The aim of the discipline Polyclinic Therahy is to improve knowledge and training students for the practice in primary healthcare.
Purposes:
- to develop students'
skills for work with outpatients that includes diagnostics and treatment
of the most common therapeutic diseases, assessing prognosis, disability, and
prophylactic medical examination;
- to
provide students' knowledge and skills for healthcare organization in
polyclinics;
- to
provide students' knowledge and skills for
the work as district internists or general practitioners;
- to improve students'
knowledge and skills for emergency care at pre-hospital stage in case of urgent
pathology or acute illness;
- to teach students work
for prevention of therapeutic diseases, provide health life-style models in
people;
- to provide students'
knowledge and skills in current diagnostic polyclinic facilities and their
proper use.
Volume of the discipline and types of educational activities:12 Points of Credit (432 academic hours).
Language - English.- Преподаватель: Фрейре Да Сильва Тиаго 1092163187
- Преподаватель: Адонис Бериша
- Преподаватель: Олеся Анатольевна Лесная
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Владимировна Митина
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Ивановна Русанова
- Преподаватель: Николай Владимирович Стуров
- Преподаватель: Андрей Валентинович Сыров
Pharmacology can be defined as the study of substances that interact with living systems through chemical processes, especially by binding to regulatory molecules and activating or inhibiting normal body processes. These substances may be chemicals administered to achieve a beneficial therapeutic effect on some process within the patient or for their toxic effects on regulatory processes in parasites infecting the patient. Such deliberate therapeutic applications may be considered the proper role ofmedical pharmacology, which is often defined as the science of substances used to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease.Toxicology is that branch of pharmacology which deals with the undesirable effects of chemicals on living systems, from individual cells to complex ecosystems.
* Bertram G. Katzung-Basic & Clinical Pharmacology(9th Edition).
The purpose of the discipline Pharmacology is to develop in students the system of knowledge about the principles of drugs classification, their mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects, indications and contraindications for use; the principles of combining drugs, the risk of adverse side effects and their prevention, rules of drugs prescription and drug rational administration.
Aims:
- To study the general laws of the drug effects on the human body: the concept of pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, pharmacodynamics of drugs, the main and adverse pharmacological effects and their dependence on the physicochemical properties of the active substance, routes of administration, species, age and condition of the animal and other conditions.
-To study classification of substances according to pharmacological groups on the basis of the systematic principle; for each group to study the general characteristics, mechanism of action, effects, indications and contraindications to the use of basic drugs, possible cases of poisoning and first aid measures.
- To know the characteristics of the individual drugs, to know their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters, mechanisms of action, the main and adverse drug effects, indications and contraindications.
- Преподаватель: Ольга Игоревна Бутранова
- Преподаватель: Элина Аркадьевна Коровякова
Gynecology or gynаecology is the branch of medicine dealing with the health of the female reproductive system (vagina, uterus and ovaries) and the breast. Literally, outside medicine, it means "the science of women". The word "gynecology" came from the Greek Γυναικ - woman and λογοζ – study. This science is anatomical, physiological, physical and mental characteristics of the female body and their disorders. Gynaecology is inextricably linked with obstetrics. Until the XIX century. these sciences were not divided - the doctrine of female diseases was part of the doctrine of obstetrics.
- Преподаватель: Said M. Semyatov
The
discipline "Professional
diseases (Occupational Diseases)" specialty 31.05.01
"Medicine" is taught in
Russian and English at the Department of Hospital Therapy with courses of
endocrinology, hematology and clinical laboratory diagnostics of the Medical Institute
of the RUDN University. The complex of the discipline is 72 hours and
includes classroom activities (48 hours) and self-study work (24 hours). In
each section of the discipline "Occupational Diseases", an etiology,
pathogenesis, clinics, differential diagnosis, clinical and labor prognosis,
modern methods of examination, treatment, prevention of occupational diseases,
principles of organizing and conducting medical examinations, issues of
examination of work capacity and clinical examination are
being studied. During study students form professional medical and
general cultural competencies. The educational-methodical complex and the work
program of the discipline are compiled in accordance with the Federal State
Educational Standard of Higher Education in specialty 31.05.01 "Medicine”. Educational
program 31.05.01 "Medicine".
- Преподаватель: Марина Робертовна Александрова
- Преподаватель: МИЛЕНА ВИВЕРОС
- Преподаватель: Николай Дмитриевич Кислый
- Преподаватель: Алексей Юрьевич Мартынов
- Преподаватель: Ольга Ивановна Тарасова
- Преподаватель: Вероника Микаэловна Ботчей
- Преподаватель: Мария Владимировна Гринберг
- Преподаватель: Маргарита Гурьевна Костяева
- Преподаватель: Ольга Борисовна Саврова
- Преподаватель: Моджисола Ибитайо Даниэл-Абу
- Преподаватель: Мария Александровна Жесткова
- Преподаватель: Мария Александровна Жесткова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Юрьевна Илларионова
- Преподаватель: Марина Григорьевна Кантемирова
- Преподаватель: Максим Александрович Карпенко
- Преподаватель: Юлия Юрьевна Новикова
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Юрьевич Овсянников
- Преподаватель: Павел Александрович Фролов
- Преподаватель: Мустафа Халед
Purpose of the discipline:
Training of practical skills, which are required by the general practitioner. The whole training course is held according to the contemporary guidelines of the European Resuscitation Council.
Main tasks of the discipline:
The main aim of this discipline is to enhance the performance of practical skills, based on earlier gained theoretical knowledges on diagnostics and treatment of patients with different diseases. This course is directed to improve the quality of provision of first aid in different emergency situations, which can be faced by the general practitioner in every day practice.

- Преподаватель: Лия Георгиевна Ахуба
- Преподаватель: Илья Сергеевич Никитин
- Преподаватель: Жанна Геннадьевна Тигай
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Шек
- Преподаватель: Александр Алексеевич Бархударов
- Преподаватель: Алексей Евгеньевич Климов
- Преподаватель: Михаил Юрьевич Персов
- Преподаватель: Оксана Николаевна Черепанова
- Преподаватель: Александр Алексеевич Бархударов
- Преподаватель: Алексей Евгеньевич Климов
- Преподаватель: Михаил Юрьевич Персов
- Преподаватель: Оксана Николаевна Черепанова
- Преподаватель: Мария Николаевна Острецова
- Преподаватель: Алексей Леонидович Савастенко
- Преподаватель: Наталья Сергеевна Сергеева
Purpose of the practice:
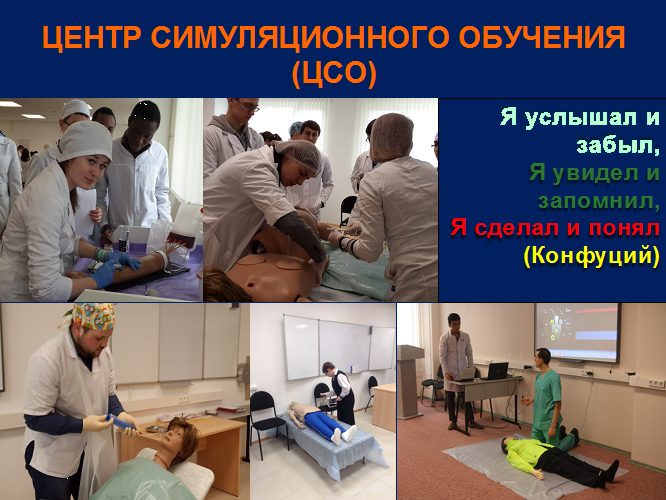
Training of basic organisational, medical, prophylactic and practical skills, including emergency aid, which are neccessary for doctors, such as: surgeon, therapist and obstetrician-gynecologist in the virtual hospital of the Simulation Training Centre.
Main tasks of the practice:
- Introduction to the job of surgical, therapeutic and gynecological departments
- Training of basic diagnostic, medical and prophylactic practical skills on high-fidelity simulators of the virtual hospital of Simulation Training Centre
- Provision of emergency aid
- Provision of prophylactic and sanitary-educative work with the population

- Преподаватель: Лия Георгиевна Ахуба
- Преподаватель: Анна Игоревна Бадретдинова
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Клименко
- Преподаватель: Илья Сергеевич Никитин
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Олегович Остаев
- Преподаватель: Жанна Геннадьевна Тигай
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Шек
Purpose of the practice:
Training of basic nursing responsibilities. Implementation of theoretical nursing knowledges in practice in the virtual hospital of the Simulation Training Centre.
Main tasks of the practice:
- Basics of asepsis and antisepsis during nursing procedures
- Doctor's assistance during different medical procedures
- Provision of nursing procedures and their registration
- Parenteral drug's administration
- Take of venous blood for different laboratory examinations
- Decontamination of syringes and other medical instruments, provision of pre- and sterilisational procedures
- Basic life support
- Registration of complications during medical procedures
- Registration of used drugs and instruments
- Observation of basic rules of sanitary-antiepidemic regime and prophylaxis of viral hepatitis B, C and HIV/AIDs

- Преподаватель: Лия Георгиевна Ахуба
- Преподаватель: Анна Игоревна Бадретдинова
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Клименко
- Преподаватель: Илья Сергеевич Никитин
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Олегович Остаев
- Преподаватель: Жанна Геннадьевна Тигай
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Шек
Purpose of the practice:
Introduction to the hospital work. Basics of deontological rules. Training of basic caring skills for therapeutic and surgical patients in the virtual hospital of the Simulation Training Centre.
Main tasks of the practice:
- Basics of the junior medical staff work
- Basics of caring for therapeutic patients
- Primary cleaning of the patient in the admission department
- Feeding of the patient. Nasogastral feeding.
- Basics of caring for patients with cardiovascular diseases
- Basics of caring for patients in the Intensive Care Unit
- Transportation of patients
- Preparation of surgical patients (enema administration, women/men urinary catheterisation).
- Changing of bed sheets and clothes

- Преподаватель: Лия Георгиевна Ахуба
- Преподаватель: Анна Игоревна Бадретдинова
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Клименко
- Преподаватель: Илья Сергеевич Никитин
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Олегович Остаев
- Преподаватель: Жанна Геннадьевна Тигай
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Шек
Short description of the course:
- Organization of the hospital.
- Organization and work of the therapeutic department.
- Organization of nursing stations; nurses responsibilities. Medical documentation.
- Basic rules of working in the therapeutic department. Features of nursing in the intensive care unit.
- Ward's hygiene. Personal hygiene.
- Nutrition of patients. The concept of clinical nutrition and dietary tables. Feeding of seriously ill patients.
- Thermometry. The concept of a fever. Types of fevers. Methods of body's temperature measuring. Thermometry blanks.
- Methods of drugs administration.
- Observation and care for patients with respiratory diseases.
- Observation and care for patients with circulatory system diseases.
- Observation and care for patients with digestive system diseases.
- Observation and care for patients with liver diseases.
- Observation and care for patients with kidney and urinary tract diseases.
- Care for seriously ill and moribund patients. Prevention of bedsores.
- Basics of Resuscitation: CPR, artificial ventilation "mouth to mouth", or "mouth to nose".
- Преподаватель: Лия Георгиевна Ахуба
- Преподаватель: Анна Игоревна Бадретдинова
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Клименко
- Преподаватель: Илья Сергеевич Никитин
- Преподаватель: Анатолий Олегович Остаев
- Преподаватель: Жанна Геннадьевна Тигай
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Шек
 The discipline "Hospital Therapy",
specialty 31.05.01 "Medicine" is taught in
Russian and English at the Department of Hospital Therapy with courses of
hematology, endocrinology and clinical laboratory diagnostics of the medical
institute of the RUDN University. The total amount of the discipline is 432 hours and includes classroom hours (288 hours) and self-study work (144 hours). The purpose of the study is to
acquire students’ knowledge of the discipline "Hospital Therapy": the
ability to make a correct diagnose, to make a differential diagnosis with
similar diseases, to determine the clinical prognosis for a particular patient,
to know the modern methods of examination, treatment and prevention, and the
formation of professional medical and general cultural competencies. The
educational-methodical complex and the work program of the discipline are
compiled in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of Higher
Education in specialty 31.05.01 "Medicine”.
The discipline "Hospital Therapy",
specialty 31.05.01 "Medicine" is taught in
Russian and English at the Department of Hospital Therapy with courses of
hematology, endocrinology and clinical laboratory diagnostics of the medical
institute of the RUDN University. The total amount of the discipline is 432 hours and includes classroom hours (288 hours) and self-study work (144 hours). The purpose of the study is to
acquire students’ knowledge of the discipline "Hospital Therapy": the
ability to make a correct diagnose, to make a differential diagnosis with
similar diseases, to determine the clinical prognosis for a particular patient,
to know the modern methods of examination, treatment and prevention, and the
formation of professional medical and general cultural competencies. The
educational-methodical complex and the work program of the discipline are
compiled in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of Higher
Education in specialty 31.05.01 "Medicine”.
- Преподаватель: Марина Робертовна Александрова
- Преподаватель: МИЛЕНА ВИВЕРОС
- Преподаватель: Ирина Алексеевна Жирова
- Преподаватель: Николай Дмитриевич Кислый
- Преподаватель: Алексей Юрьевич Мартынов
- Преподаватель: Николай Игоревич Стуклов
- Преподаватель: Ольга Ивановна Тарасова
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Лукьянова
- Преподаватель: Татьяна Владимировна Ляпунова
- Преподаватель: Екатерина Михайловна Шимкевич
- Преподаватель: Елена Анатольевна Лукьянова
- Преподаватель: Мадина Гаруновна Буржунова
Topographic anatomy and operative surgery is a obligatory subject, the teaching of which is held on the 3rd and 4th year (6-7 semesters). Discipline includes the general part studies the general questions of topographic anatomy and operative surgery and a special section, which includes the study of topographic anatomy and operative surgery of regions of the human body.
- Преподаватель: Андрей Витальевич Протасов
- Преподаватель: Дмитрий Леонидович Титаров
- Преподаватель: Александра Андреевна Косорукова
- Преподаватель: Ольга Владимировна Саввина
Objectives and targets
To provide students of medical students with knowledge of key concepts of modern economic theories
To introduce students of medical faculty to basic categories of economic theories; give a general idea of ways of Russian and world economy in terms of globalization, to form the understanding of current problems of creating modern economy’s institutional structure
Place of the discipline in the structure of Obligatory General Studies:
The discipline “Economics’ is a basic part for specialty 31.05.01 “General Health” of C.1.B.4 cycle of educational program for “General Health” students. The program of the course is based on assumption, that medical faculty students need to know basic concepts of modern economics based on the knowledge of world and national history
- Преподаватель: Ани Ашотовна Оганесян
- Преподаватель: Ханифа Витальевна Тыркба
Materials of the "Phthisiatry" discipline (in english) contain basic information on the etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of tuberculosis, in accordance with Federal state educational standards of higher professional education.
Enter as guest. Login: student Password: St_54321
- Преподаватель: Владимир Анатольевич Кошечкин
- Преподаватель: Александра Александровна Савосина
- Преподаватель: Светлана Николаевна Суслина
- Преподаватель: Анна Сергеевна Хомик
- Преподаватель: Алексей Васильевич Швец
- Преподаватель: Алимат Мусса-Алиевна Эбзеева
The Biochemistry course explores the molecular nuts and bolts of living organism, with particular emphasis on disease and avenues for therapy.
- Преподаватель: Ольга Матвеевна Кузнецова

